Overview
Face morphing involves an understanding of corresponding points and how that alignment can be manipulated to produce a warped image that can produce a face-morphing affect.
Part 1: Defining Correspondences
The first step was to identify the two images that are being warped and to label the points that are corresponding. In my example, I used the tool developed by another student in the previous year to match each point labeled on both images. I then used Delaunay library from scipy. to determine the triangulation based on the given points. That then produces the following images.
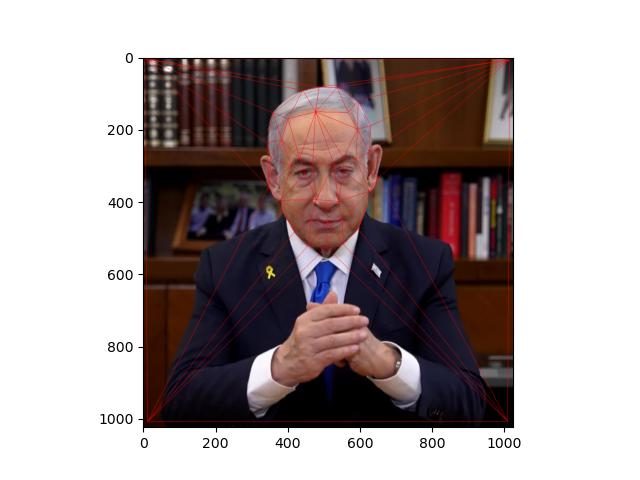

|
|
Part 2: Computing the "Mid-way Face"
The next step is to develop a method that morphs an image. The algorithm of this function is that for each triangle in the source image, the corresponding area is warped to fit the target triangle, and this is repeated for all triangles. By doing this, the face image is transformed to fit an average shape. The warping aspect requires another functionality that calculates the affine matrix transformation. By doing this process on each image and passing in the same triangulation from the previous part, it will warp each image to eachother creating a form of a hybrid.
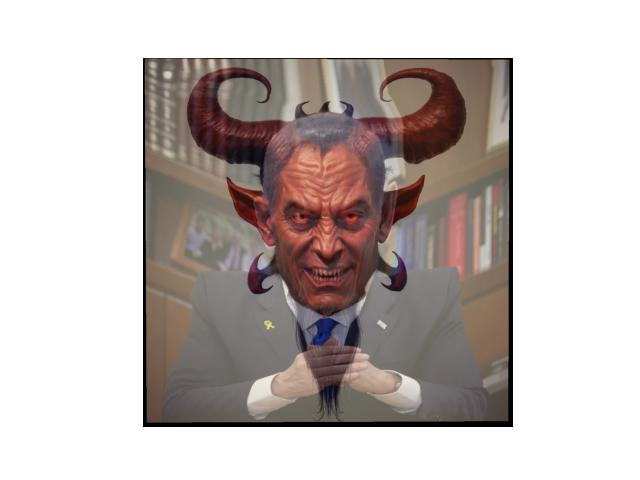

|
Part 3: The Morph Sequence
Now that the basic functionality has been implemented, we can create a morph sequence by adjusting the amount that the points from each image are weighted.

|
Part 4: The "Mean Face" of a population
For this part, I used the Danes dataset provided in Danes where I was given 37 images of people's faces. For each face, I was given the jpg of the face and an asf file that has the information of points that outline the features of the faces. After extracting the points from each image, I took the average to have that will be used as the average shape. Then, I warped each image from the data to that average shape.
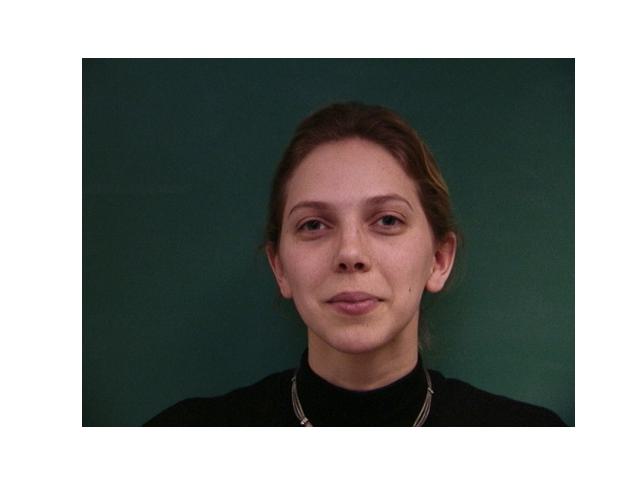

|
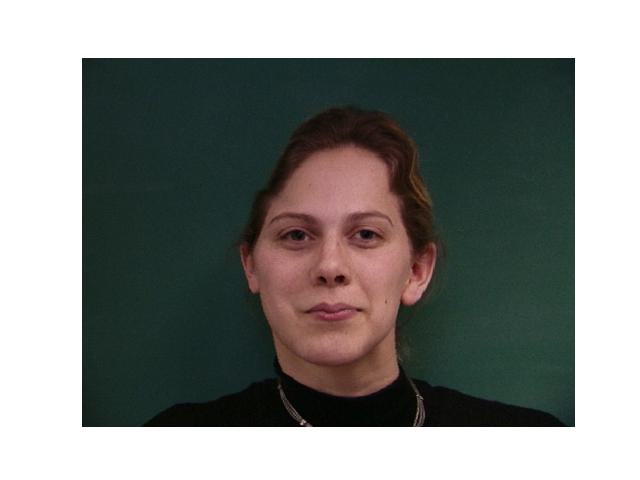

|
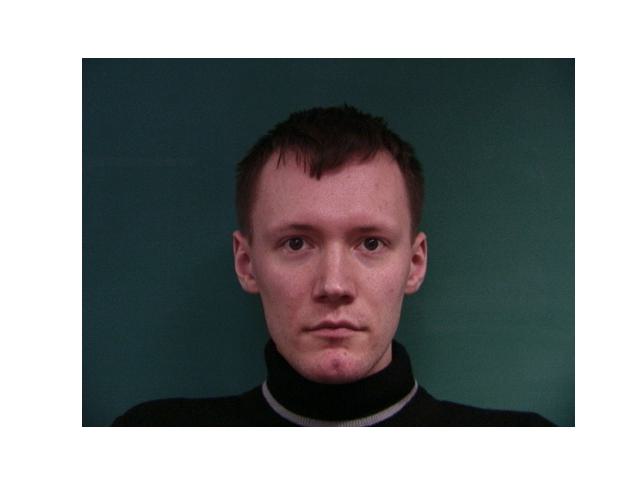

|
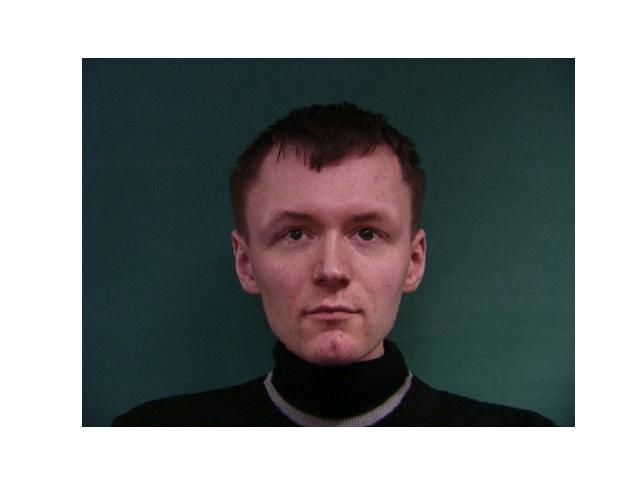

|
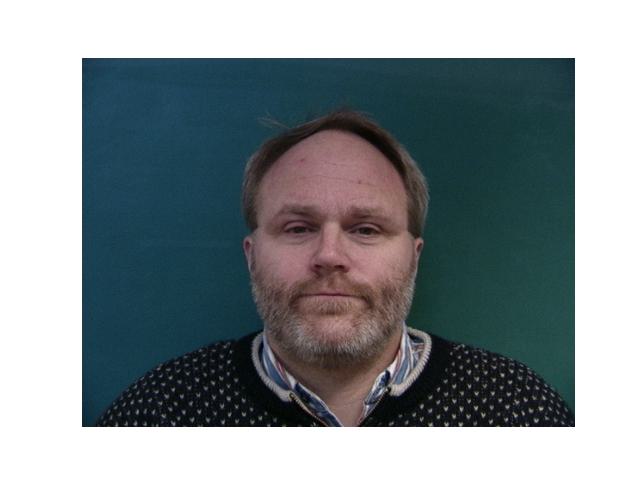

|
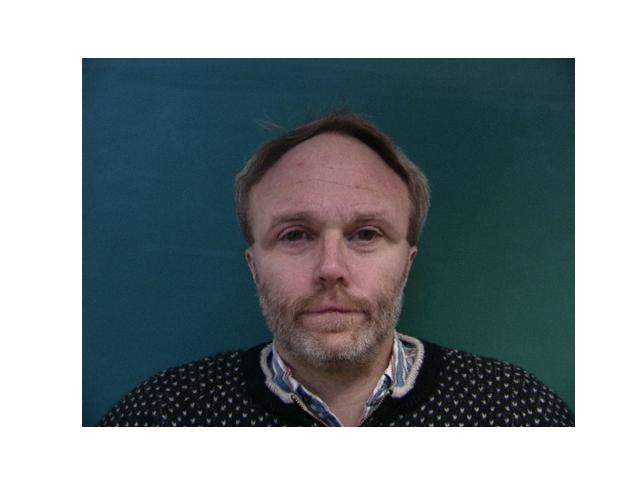

|
I can take all the morphed images and find the average which will produce a very symmetrical result.
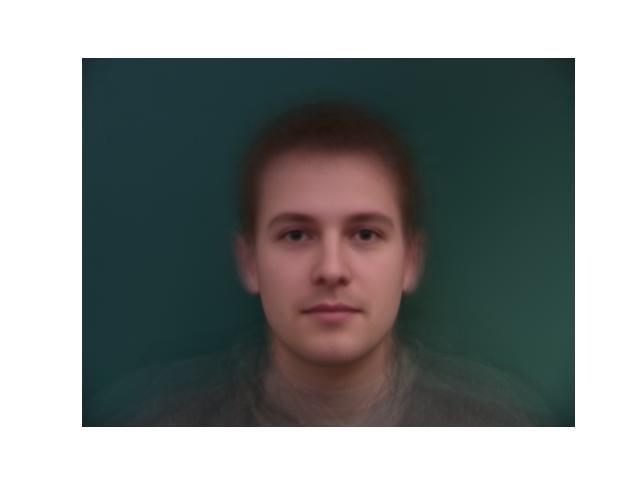

|
Now, I will take an image of my face and map the corresponding points. Then, I can morph my face and the points to the average shape of points from the dataset.
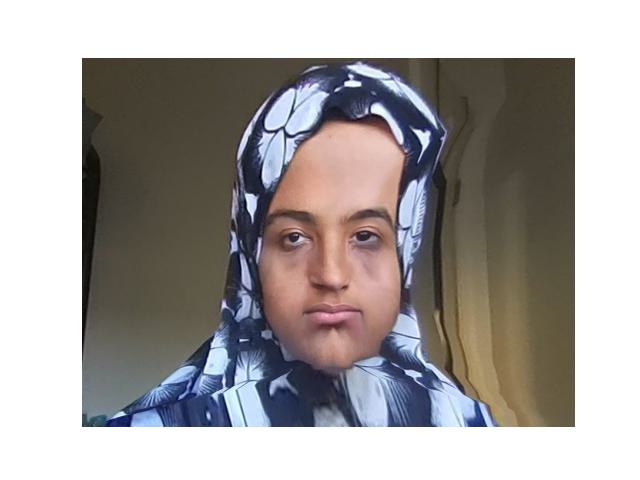

|
I can even take the average shape of points of my face and morph the average image from the data to my face.
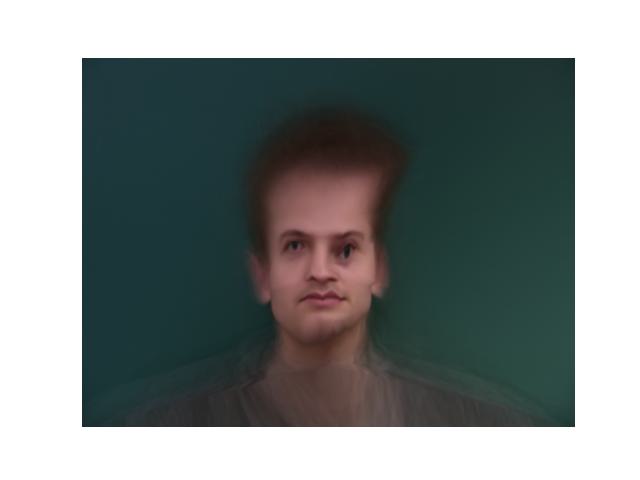

|
Part 5: Caricatures - Extrapolating from the Mean
By using the calculations from the previous part, I can adjust the value that determined how much to morph each image to the other to be either less than 0 or greater than 1. When the value is less than 0, it will exaggerate the features on my face. For values greater than 1, it will exaggerate the features on the average image.
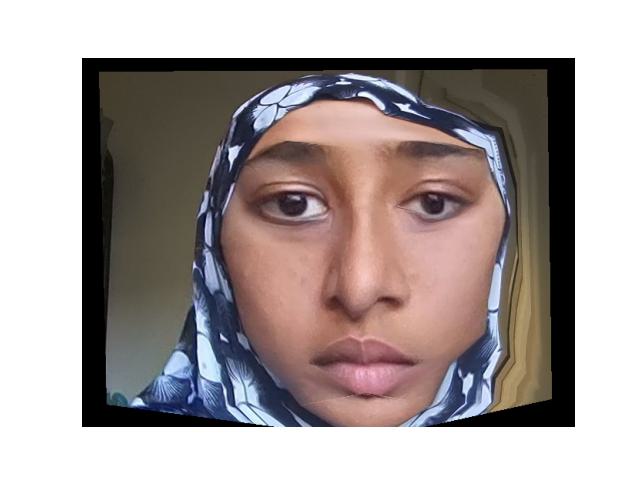

|
Bells and Whistles
I created a music video with all my passport pictures morphing into eachother. The last time I got a passport picture was when I was 10.